Economy
Renewable power capacity stalls for 1st time since turn of millennium
The current situation and prospects of solar energy in Hungary, including changes to the regulatory environment will also be on the agenda of the Portfolio Clean Energy & Disruptive Trend Summit 2019 conference on 4 June. It’s not too late to register!
Last year was the first time since 2001 that growth in renewable power capacity failed to increase year on year. New net capacity from solar PV, wind, hydro, bioenergy, and other renewable power sources increased by about 180 Gigawatts (GW) in 2018, the same as the previous year, according to the International Energy Agency’s latest data.
That’s only around 60% of the net additions needed each year to meet long-term climate goals.
Renewables have a major role to play in curbing global emissions. Renewable capacity additions need to grow by over 300 GW on average each year between 2018 and 2030 to reach the goals of the Paris Agreement, according to the IEA’s Sustainable Development Scenario (SDS).
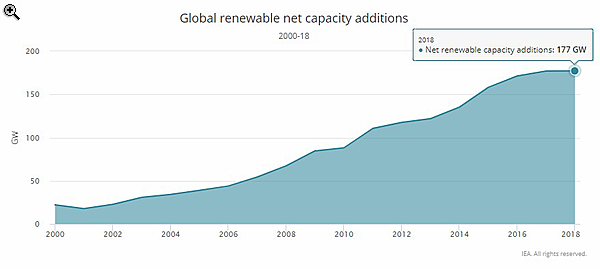
Since 2015, global solar PV’s exponential growth had been compensating for slower increases in wind and hydropower. But solar PV’s growth flattened in 2018, adding 97 GW of capacity and falling short of expectations it would surpass the symbolic 100 GW mark.
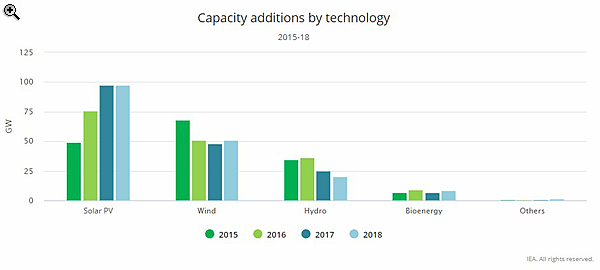
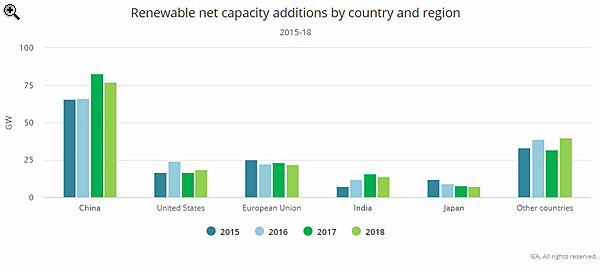
Capacity additions in the European Union, the second-largest market for renewables, saw a slight decline. Solar PV grew compared with the previous year, while wind additions slowed down. Policy transition challenges and changing renewable incentives resulted in slower growth of onshore wind in India and of solar PV in Japan.
Renewable capacity expansion accelerated in many emerging economies and developing countries in the Middle East, North Africa and parts of Asia, led by wind and solar PV as a result of rapid cost declines.

The current situation and prospects of solar energy in Hungary, including changes to the regulatory environment will also be on the agenda of the Portfolio Clean Energy & Disruptive Trend Summit 2019 conference on 4 June. It’s not too late to register!>
Cover photo by Shutterstock
Cover photo by Shutterstock
More in Economy
December 04, 2025 16:10
This is what we should expect after the new Hungarian wage agreement
There are risks associated with forced wage increases
December 04, 2025 15:10
Here's the most important table on Hungary's 2026 minimum wage hike
Let's see out how much greater the gross amount will be
December 04, 2025 12:23
More people in Hungary admitted to hospital with respiratory infections
But the situation is still a lot better than in the past two seasons
December 04, 2025 10:09
Hungarian food industry lags 20-25 years behind: can it catch up?
A new era begins, said the participans of a roundtable discussion at Portfolio's Agricultural Conference
December 04, 2025 09:40
Moderate growth in Hungary's retail sales continue
This is the second set of data that gives us an idea of the Q4 economic performance
December 04, 2025 09:10
Analysts revise forecasts due to warning signs emerging from the Hungarian economy
Statistical office carries out marked revision of GDP data
LATEST NEWS








